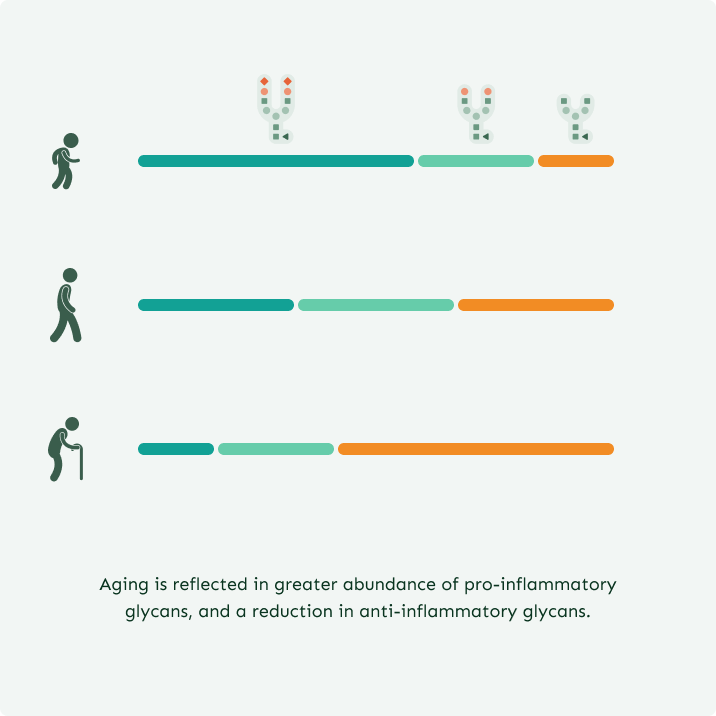Partnering with top universities, we’ve built the largest glycan research program in the world, discovering how these molecules reveal deep insights about health, aging, and resilience.
ANALYZING GLYCANS
We Are Unique In What We Do
GlycanAge is the only biological age test in the world that measures chronic inflammation by analyzing glycans, a powerful but often overlooked layer of biology that influences immune function, and overall health.
Backed by 30+ years of research, GlycanAge sits at the frontier of personalized, preventative health, translating cutting-edge glycoscience into real-world insights you can act on.
LANGUAGE OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
What Are Glycans Anyway?
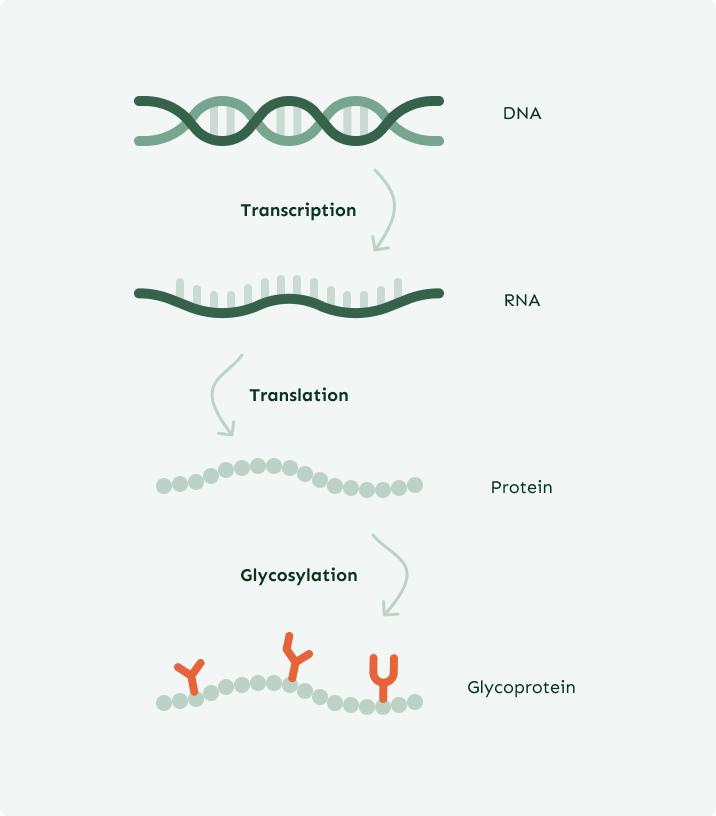
Glycans are complex sugars and one of life’s four essential building blocks, alongside proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. They coat every cell surface and are attached to over half of all human proteins, regulating immunity, cell signaling, and development.
At GlycanAge, we study a specific group of glycans on Immunoglobulin G (IgG), the main protective antibody. These glycans act like switches, turning immune activity up or down, and are closely linked to inflammation and long-term health.
Unlike standard tests that detect issues only after their onset, glycans reveal early signs of immune imbalance and chronic inflammation, well before symptoms appear. That’s what makes them the foundation of true prevention.
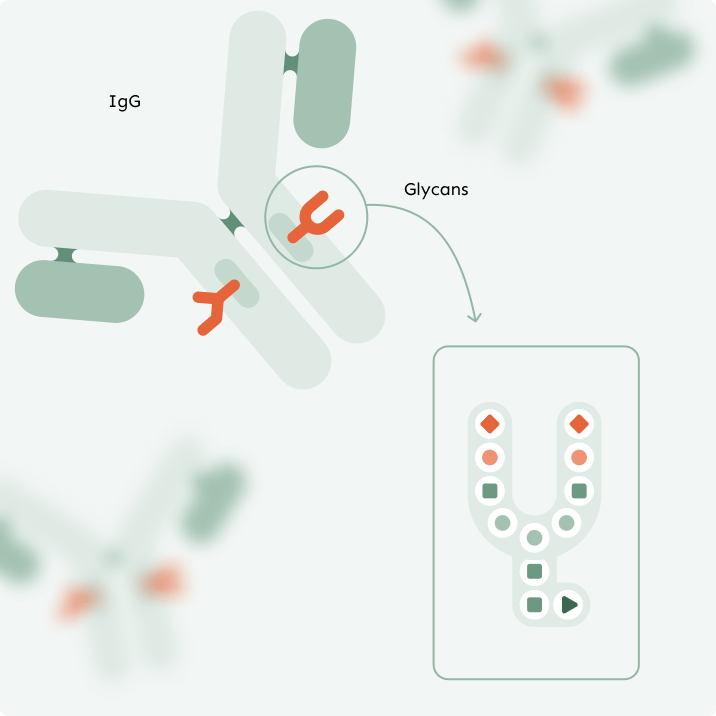
A WINDOW INTO INFLAMMATION
What Do Glycans Reflect?
IgG glycans are the only biomarker that accurately reflects chronic inflammation—a key hallmark of aging and an early sign of immune imbalance.
As we age, immune regulation declines, leading to persistent, low-grade inflammation, or “inflammaging.” This drives age-related diseases and is strongly influenced by lifestyle factors like stress, poor sleep, poor diet, and inactivity.
Chronic inflammation captures the combined influence of genetics, epigenetics, environment, and lifestyle—all in one measurable signal. That’s why it’s one of the most powerful indicators of biological age and future health risk.
IgG glycans are the only way to accurately measure chronic inflammation, offering a unique, early, and actionable window for prevention.
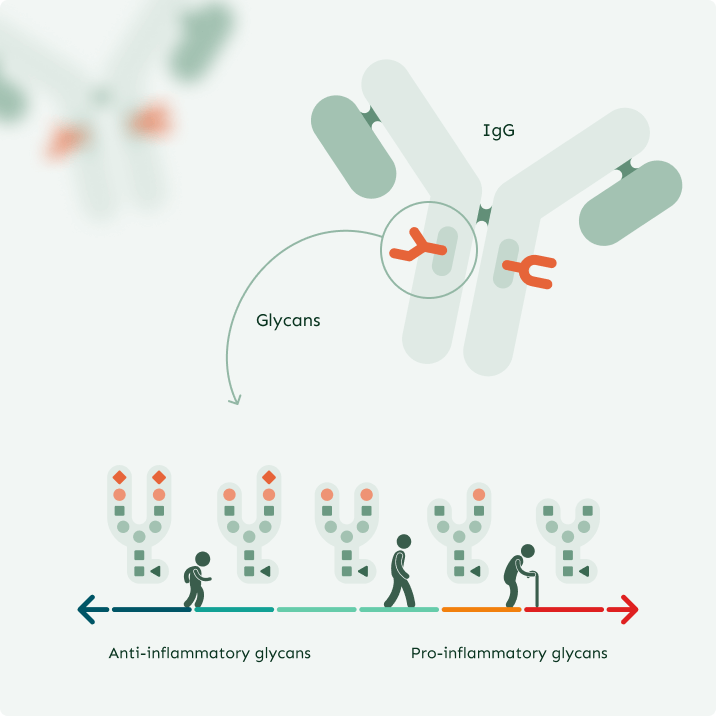
MEASURING IMMUNE RESILIENCE
How Do We Determine Biological Age?
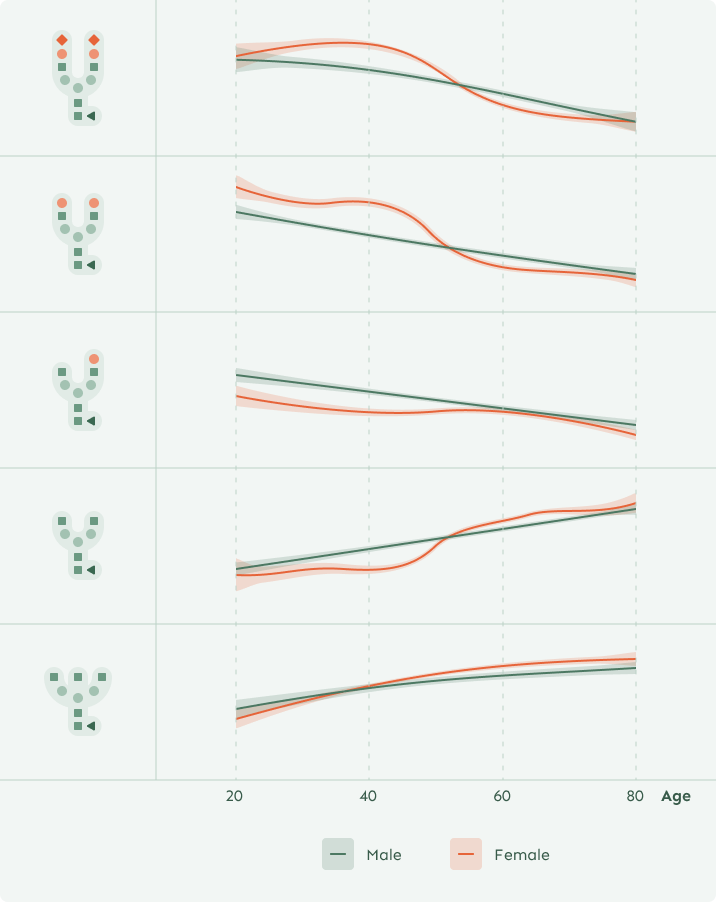
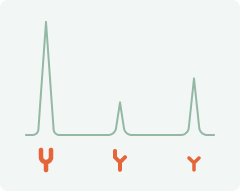
Everyone has their unique IgG glycome—the collection of glycans attached to IgG antibodies.
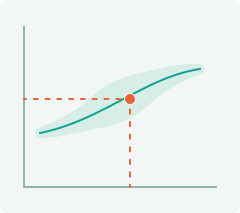
While we share the same glycan types, the ratios of these glycans vary from person to person. In youth, anti-inflammatory glycans dominate, but with aging, disease, and unhealthy habits, this balance shifts toward pro-inflammatory glycans.
By measuring the balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory glycans, we can determine a person’s biological age, viewed through the lens of the immune system.