Top 12 Anti Inflammatory Teas to Improve your Health
What teas are good for inflammation? What teas are anti-inflammatory? Click here to discover the best anti-inflammatory herbs for tea.
What is Inflammation?
Inflammation is the body's natural response to injury or infection, acting as a protective measure to remove harmful stimuli and promote healing. However, chronic inflammation can become a problem, leading to various health issues such as arthritis, heart disease, and even cancer.
One delicious and natural way to combat inflammation is by consuming anti-inflammatory teas. Teas have been consumed for centuries for their numerous health benefits and are gaining increased recognition for their anti-inflammatory properties.
In this article, we will explore:
- The science behind how these teas help fight inflammation
- The best herbal teas for inflammation relief
- The health benefits of consuming anti-inflammatory herbal teas
- Useful tips and precautions for tea drinkers
How Is Tea Good For Inflammation?
Tea contains a variety of bioactive compounds, such as polyphenols, catechins, and flavonoids, which have been shown to possess anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-carcinogenic properties.
 These compounds work by modulating various signalling pathways and reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, ultimately helping to alleviate inflammation.
These compounds work by modulating various signalling pathways and reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, ultimately helping to alleviate inflammation.
By helping to reduce inflammation through these mechanisms, tea can alleviate symptoms associated with various inflammatory conditions, such as arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and certain cancers.
Best Anti Inflammatory Teas
Green Tea
 Green tea is one of the most widely consumed teas worldwide, known for its numerous health benefits. It is rich in catechins, particularly epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which has potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Studies have shown that green tea can help reduce inflammation associated with arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and certain cancers.
Green tea is one of the most widely consumed teas worldwide, known for its numerous health benefits. It is rich in catechins, particularly epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), which has potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Studies have shown that green tea can help reduce inflammation associated with arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and certain cancers.
Turmeric Tea
 Turmeric is a popular spice with a long history of use in Ayurvedic and traditional Chinese medicine. The active compound in turmeric, curcumin, has been extensively studied for its anti-inflammatory properties.
Turmeric is a popular spice with a long history of use in Ayurvedic and traditional Chinese medicine. The active compound in turmeric, curcumin, has been extensively studied for its anti-inflammatory properties.
Its anti-inflammatory effects have been linked to the prevention and management of various chronic inflammatory conditions, such as neurodegenerative diseases and certain cancers, such as lung, breast, and prostate.
It is often recommended to consume turmeric tea with a small amount of black pepper, which contains piperine, a compound that increases the absorption of curcumin in the body.
Ginger Tea
 Ginger has been used for centuries in various traditional medicine systems to treat a wide range of ailments owing to its high antioxidant content.
Ginger has been used for centuries in various traditional medicine systems to treat a wide range of ailments owing to its high antioxidant content.
The bioactive compounds in ginger, such as gingerols and shogaols, can help reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms of inflammatory conditions like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, as well as post-exercise inflammation.
Rooibos Tea
 Rooibos is a South African herbal tea that has gained popularity for its unique taste and health benefits. It is rich in polyphenols, such as aspalathin and nothofagin, which have been shown to possess anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Rooibos is a South African herbal tea that has gained popularity for its unique taste and health benefits. It is rich in polyphenols, such as aspalathin and nothofagin, which have been shown to possess anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Regular consumption of rooibos tea may alleviate symptoms of chronic inflammatory diseases and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
White Tea
 White tea, like green tea, is derived from the Camellia sinensis plant but is less processed, allowing it to retain higher levels of antioxidants, such as catechins.
White tea, like green tea, is derived from the Camellia sinensis plant but is less processed, allowing it to retain higher levels of antioxidants, such as catechins.
White tea is also lower in caffeine than green or black tea, making it a suitable option for people who want to minimise their caffeine intake while still obtaining anti-inflammatory benefits.
Chamomile Tea
 Chamomile is a popular herbal tea known for its calming effects and numerous health benefits. The key anti-inflammatory compounds in chamomile include apigenin, luteolin, and bisabolol.
Chamomile is a popular herbal tea known for its calming effects and numerous health benefits. The key anti-inflammatory compounds in chamomile include apigenin, luteolin, and bisabolol.
Regular consumption of chamomile tea may help alleviate symptoms of inflammatory conditions such as gastrointestinal disorders and skin inflammation.
Peppermint Tea
 Peppermint is an aromatic herb that has been widely used in traditional medicine for its digestive and soothing properties. It contains bioactive compounds like menthol, menthone, and rosmarinic acid.
Peppermint is an aromatic herb that has been widely used in traditional medicine for its digestive and soothing properties. It contains bioactive compounds like menthol, menthone, and rosmarinic acid.
Drinking peppermint tea may help ease digestive issues and relieve symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome as well as tension headaches and migraines.
Tulsi Tea (Holy Basil)
 Tulsi, also known as holy basil (Ocimum sanctum), is an aromatic herb used extensively in Ayurvedic medicine.
Tulsi, also known as holy basil (Ocimum sanctum), is an aromatic herb used extensively in Ayurvedic medicine.
The key compounds in tulsi, such as eugenol, rosmarinic acid, and ursolic acid, may help ease joint inflammation, lower blood sugar, and protect the stomach.
Consuming tulsi tea can help improve the body's response to stress, making it a beneficial addition to an anti-inflammatory diet.
Rosehip Tea
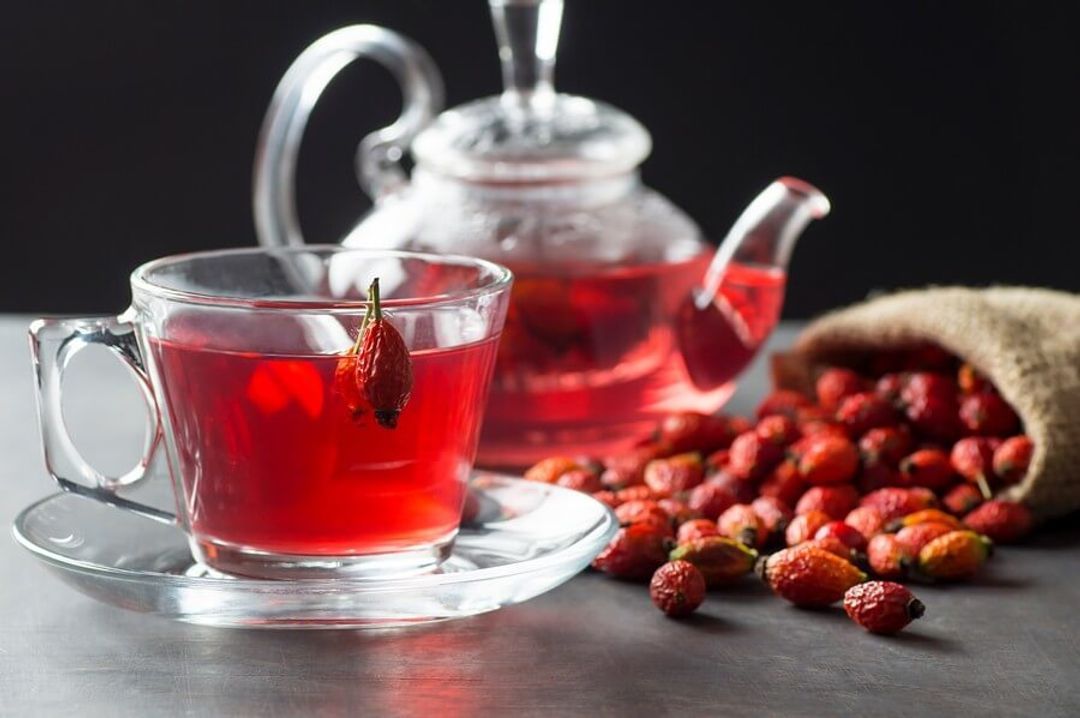 Rosehips, the fruit of the wild rose plant (Rosa canina), are a rich source of vitamin C, E, beta carotene, and other bioactive compounds like polyphenols and carotenoids.
Rosehips, the fruit of the wild rose plant (Rosa canina), are a rich source of vitamin C, E, beta carotene, and other bioactive compounds like polyphenols and carotenoids.
These compounds have been shown to possess properties that protect cells from damage.
Drinking rosehip tea may help alleviate joint pain and promote skin health.
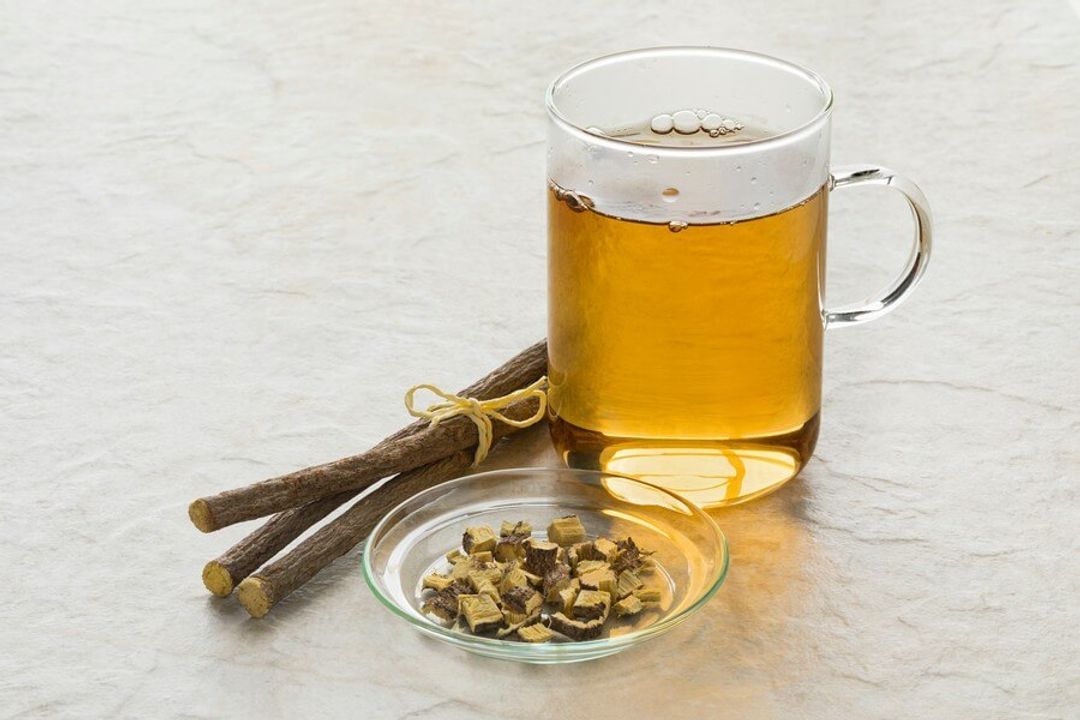 Liquorice Root Tea
Liquorice Root Tea
Liquorice root (Glycyrrhiza glabra) has been used in traditional medicine for its soothing and anti-inflammatory effects. Drinking liquorice root tea also promotes digestive health.
The active compound in liquorice root, glycyrrhizin, has potent anti-inflammatory properties. Studies have shown it can help reduce inflammation in conditions like gastritis, peptic ulcers, and respiratory issues.
Lemon Balm Tea
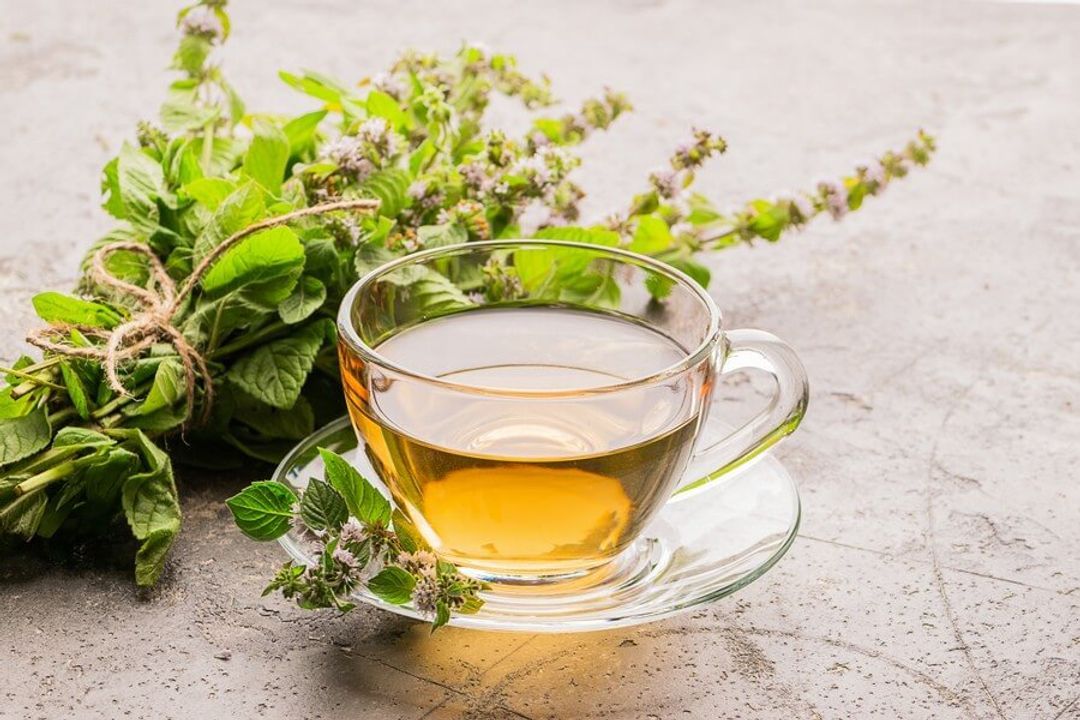 Lemon balm (Melissa officinalis) is a perennial herb from the mint family native to Europe, North Africa, and West Asia. It has been used in traditional medicine for its calming, digestive, and anti-inflammatory properties.
Lemon balm (Melissa officinalis) is a perennial herb from the mint family native to Europe, North Africa, and West Asia. It has been used in traditional medicine for its calming, digestive, and anti-inflammatory properties.
Lemon balm contains several bioactive compounds, including terpenes, flavonoids, and phenolic acids, which contribute to its anti-inflammatory effects and may help alleviate symptoms associated with conditions such as arthritis, gastrointestinal disorders, and respiratory issues.
Additionally, it can have a calming effect on the nervous system and may help reduce anxiety and stress, which can contribute to inflammation.
Hibiscus Tea
 Hibiscus is a tropical plant known for its vibrant, trumpet-shaped flowers. Hibiscus tea, also known as "sour tea" or "roselle tea," is made from the dried calyces of the hibiscus flowers and has a tart, cranberry-like flavour.
Hibiscus is a tropical plant known for its vibrant, trumpet-shaped flowers. Hibiscus tea, also known as "sour tea" or "roselle tea," is made from the dried calyces of the hibiscus flowers and has a tart, cranberry-like flavour.
Hibiscus contains several bioactive compounds, including anthocyanins, flavonoids, and phenolic acids, which comprise its anti-inflammatory profile.
Hibiscus tea may help alleviate symptoms associated with various inflammatory conditions, such as arthritis, gastrointestinal disorders, and respiratory issues.
Additionally, it has been studied for its potential benefits in managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels, which may indirectly contribute to reducing inflammation.
Health Benefits Of Anti Inflammatory Tea
The health benefits of consuming anti-inflammatory teas extend beyond their ability to reduce inflammation. Some of these benefits include:
Improved Heart Health
 Anti-inflammatory teas can help improve heart health by reducing inflammation in blood vessels, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels. Additionally, the antioxidants present in these teas can protect against oxidative stress, a key factor in the development of heart disease.
Anti-inflammatory teas can help improve heart health by reducing inflammation in blood vessels, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels. Additionally, the antioxidants present in these teas can protect against oxidative stress, a key factor in the development of heart disease.
Enhanced Immune Function
By modulating the immune response and reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, anti-inflammatory teas can help strengthen the immune system and make it more resilient against infections and other diseases.
Weight Management
Some anti-inflammatory teas, such as green tea, have been shown to promote weight loss by increasing metabolism and fat oxidation. Moreover, reducing inflammation may help prevent weight gain by improving insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism.
Reduced Cancer Risk
The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of these teas can help protect against the development and progression of certain types of cancer, such as ovarian, liver, colorectal, skin, and prostate, by inhibiting the growth of cancer cells, reducing inflammation, and preventing DNA damage.
Tips and Precautions for Tea Drinkers
Quality Matters
Choose high-quality, organic teas whenever possible to ensure the tea is free from pesticides and other contaminants. Additionally, opt for loose-leaf tea rather than tea bags, as the former typically contains whole tea leaves, which have higher concentrations of bioactive compounds.
Steep Time and Temperature
 Follow the recommended steeping time and temperature for each type of tea to extract the maximum amount of beneficial compounds. Oversteeping can result in a bitter taste and may destroy some of the beneficial compounds.
Follow the recommended steeping time and temperature for each type of tea to extract the maximum amount of beneficial compounds. Oversteeping can result in a bitter taste and may destroy some of the beneficial compounds.
Avoid Adding Sugar
Adding sugar to your tea can negate some of the health benefits and promote inflammation. Instead, consider using natural sweeteners such as honey, stevia, or monk fruit if needed.
Consult Your Healthcare Provider
If you have a pre-existing medical condition or are taking medications, consult your healthcare provider before incorporating anti-inflammatory teas into your routine. Some teas may negatively interact with medications or exacerbate certain health conditions.
Take Care Of Your Health with GlycanAge
Incorporating anti-inflammatory teas into your daily routine can be a delicious and natural way to combat inflammation and enjoy numerous health benefits. You can make the most of these inflammation-fighting brews by choosing high-quality teas, following proper steeping techniques, and consulting your healthcare provider when necessary.
Chronic inflammation can significantly impact biological age, accelerating the ageing process and increasing the risk of age-related diseases. Reducing inflammation through lifestyle modifications, such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep, can help slow ageing and lower the risk of age-related diseases.
Additionally, taking the GlycanAge biological age test may provide valuable insights into a person's overall health and potential risks for age-related diseases. The test measures chronic inflammation in the body based on how one’s biological age is calculated.

The test can thus help you understand what lifestyle choices are right for you and help you implement necessary changes to effectively increase your health span and even reverse the ageing process.
Once you’ve ordered your home testing kit, you must provide a small blood sample and mail it back to the lab for analysis. It’ll take 3-5 weeks to complete comprehensive tests and return a personalised report on your results.
You will also receive complimentary one-to-one consultations with a health scientist and/or healthcare professional to understand your results and make a plan to improve your overall wellness as you get older.
With various price points and payment plans available, there is an option to suit each person who wants an accurate, reliable, and affordable way to determine their health state. Start your wellness journey today - take our health quiz.
FAQ
Does drinking tea reduce inflammation?
Drinking tea has been shown to help reduce inflammation due to its rich content of bioactive compounds, such as polyphenols, flavonoids, and catechins. These compounds possess antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that help modulate inflammatory pathways and protect against cellular damage. Some popular types of tea known for their anti-inflammatory effects include green tea, white tea, turmeric tea, and ginger tea.
Which tea is the most anti inflammatory?
It's hard to choose the most anti inflammatory tea, since there are so many teas with anti inflammatory ingredients. We suggest picking the one that addresses your needs.
What is the #1 best drink to reduce inflammation?
Teas are great at reducing inflammation, and specific teas can help with specific conditions, like joint pain, IBS and such.
What tea is good for joint inflammation?
Joint inflammation can be eased with green tea, ginger tea, turmeric tea and more.
What tea is the strongest natural anti-inflammatory?
It depends on your needs. Green tea, chamomile tea, ginger tea and white tea all work amazingly in reducing inflammation.
How long does it take to reduce inflammation in the body?
The time it takes to reduce inflammation in the body can vary significantly depending on several factors, such as the underlying cause of inflammation, the severity of the condition, individual differences in genetics and metabolism, and the effectiveness of the interventions employed.
How do you get rid of inflammation fast?
While it's important to remember that reducing inflammation quickly may not always be possible, especially in the case of chronic inflammation, we know how to reduce inflammation in the body fast.
Try:
- Over-the-counter NSAIDs
- Cold therapy
- Compression bandaging
- Rest
- An anti-inflammatory diet
- Hydration
- Low-impact activities
- Stress management techniques
- Professional help


