Vitamin D3 Anti-Aging Benefits
Having sufficient vitamin D levels in our system is crucial to supporting a healthy lifestyle in our old years. Learn about some of the unexpected anti-ageing benefits of vitamin D3.
- The most efficient way for your body to manufacture vitamin D3 is through moderate sun exposure. The required amount of time in the sun will depend on various factors such as location, time of day, cloud coverage, pollution and skin melanin content.
- There are some foods which are high in vitamin D - including oily fish, eggs, red meat, liver, egg yolks, and mushrooms which have been exposed to high levels of sunlight. If you prefer a more plant based diet, there are foods which have been fortified with vitamin D and supplements.
- If you are able to maintain healthy levels of vitamin D3, it can assist with providing some anti-ageing benefits. For example, stronger bones, supporting immunity issues, hair loss, and potential weight management.
- There can be a few signs that can indicate you are suffering from a vitamin D deficiency. Symptoms can be very subtle for some, and they include bone pain, muscle weakness, fatigue and depression.
One of the first tips we are taught about slowing the signs of ageing is to limit exposure to the sun's damaging ultraviolet (UV) rays and wear protective sunscreen when exposed to sunlight. But the sun is not all harmful as it helps our bodies manufacture vitamin D3 throughout the skin. This does not give you the green light to jump outside in the midday sun to tan your skin – as only 10 to 15 minutes of sunlight exposure is enough to help our bodies get a vitamin D3 top-up.
Vitamin D3 is considered by many as the must-have essential vitamin in the anti-ageing armoury. Older people need to have sufficient vitamin D3 levels in their diet to help maintain bone strength and create healthy cells. It is found in animal food sources like fatty fish and fish oils, liver, organ meats and egg yolks. There are also many fortified foods on the market, like breakfast cereals, yoghurt, and orange juice which can be introduced to the diet to help with vitamin levels.
With research into the effects of vitamin D3 on the body well on its way, we are learning more about this powerhouse nutrient. This article uncovers some of the anti-ageing benefits vitamin D3 can offer – helping you feel healthier and look younger.
What is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D is both a hormone and nutrient we eat, which is naturally produced by our bodies. Unlike water-soluble vitamins, which are excreted by your body, vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin, so the body stores any excess vitamin it does not use. This means it is possible to top up your vitamin D levels, and the body will use it when needed.
There are two primary forms of vitamin D: D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol). Both vitamins play the same role in the body, but they have slightly different molecular structures. The main difference between the two is that vitamin D2 comes from plants, while D3 derives from animals – including humans.
Scientists are not yet sure whether one is superior to the other when it comes to human health. However, it is understood that both types can increase the vitamin D levels in the blood. Some research indicates that vitamin D3 may raise the quantity in the blood higher and for longer when compared to D2.
What is the Difference Between Vitamin D and Vitamin D3?
Vitamin D refers to a group of fat-soluble vitamins essential for calcium absorption, bone health, and immune function. Vitamin D3 is a specific form of vitamin D that the body produces naturally through sunlight exposure and is also present in animal-based foods. While both D2 and D3 serve similar functions, D3 is generally more potent and longer-lasting in the bloodstream, making it a preferred choice for supplementation.
The List of Anti-ageing Benefits of Vitamin D3

We understand that vitamin D is essential for human health. It plays a significant role in keeping our bones healthy, the nervous system, and the immune system. These are all crucial areas at every stage of life, but they may need extra attention as we age with higher vitamin D levels to slow down the ageing process.
Here are some of the leading examples of how vitamin D3 can support anti-ageing:
Fights Off Infections
Vitamin D has been shown to affect the immune system positively and could help fight age-related immunity issues. It has the potential to reduce the risk of colds, the flu and respiratory infections by up to 70%. Research into the area notably picked up during the coronavirus disease 2019 era, when extensive attention has been needed on the role of vitamins in the regulation of immunity. It was found that there is evidence for an epidemiological connection between low vitamin D levels and a variety of infectious diseases. With Covid-19 still a significant concern, especially for older people, it is no surprise that research continues, and we are encouraged to maintain healthy vitamin D levels.
Reduces Hair Loss
Many people become self-conscious about their hair as they age. It is common for people to experience hair thinning or for their hair to fall out. Various causes include the body not processing nutrients as efficiently, reduced hormonal support, and nutritional deficiencies. Vitamin D has been shown to potentially stimulate hair growth by stimulating new and old hair follicles. When the vitamin levels are too low, it can lead to new hair growth being stunted.
Helps Regulate Weight
There are a lot of theories around the connection between vitamin D and weight loss. Studies have shown that a higher body mass index and body fat percentage are associated with lower vitamin D levels in the blood. The argument around why this is the case is convoluted. Some say it is due to overweight people being less likely to eat healthy foods containing vitamin D, while others recognise the correlation between living a healthy lifestyle and spending lots of time outdoors. We understand that being overweight can result in ongoing health problems and can also lead to premature ageing, so it is best to maintain a healthy weight.
Strengthens Your Bones
One of the best-known attributes vitamin D gives to the human body is its ability to support bone health. As you get older, your body can reabsorb calcium and phosphate from your bones instead of keeping these much-needed minerals in your bones. This results in your bones becoming weaker, a condition known as osteoporosis. Vitamin D assists your body in absorbing and making use of calcium, giving your bones their strength and hardness. If your vitamin levels are low, there is an increased risk of frailty, which many of us fear with old age. Keep your vitamin D levels at a healthy level to keep your skeleton moving for longer.
Makes Skin Look Younger
Vitamin D3’s antioxidant properties combat free radicals that cause premature aging. It supports collagen and elastin production, improving skin elasticity and reducing the appearance of wrinkles. Healthy vitamin D levels promote skin rejuvenation and a youthful glow.
What are the Causes of Vitamin Deficiency?
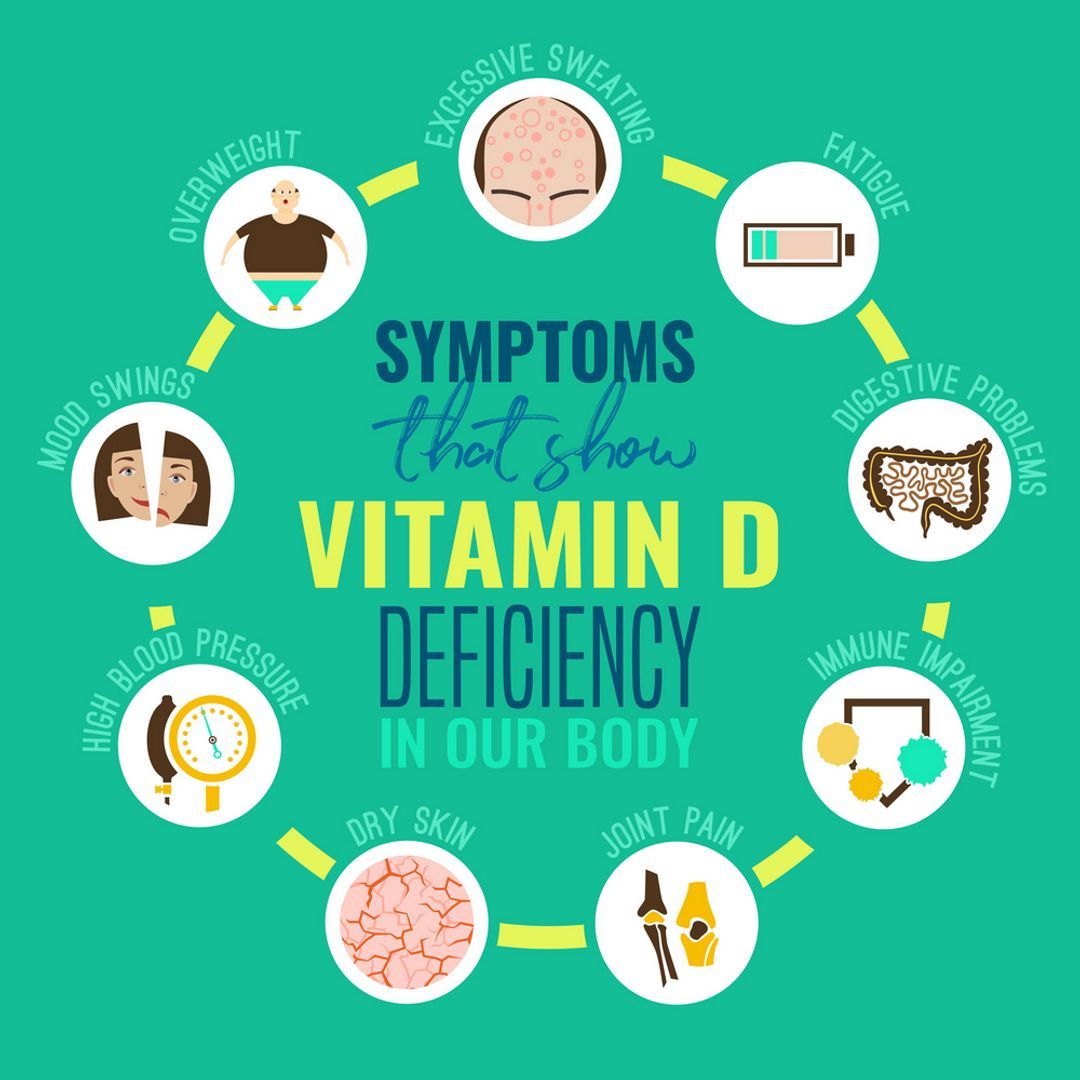
There are a few signals your body will give if you are suffering from vitamin D deficiency. Symptoms include bone pain, muscle weakness, fatigue and depression – however, these indicators can be very subtle for some people.
Vitamin D deficiency can occur due to several reasons. Here are some of the primary causes:
Low consumption
Most natural sources of vitamin D are animal-based, and those who follow a vegan diet or have special dietary requirements may not be able to consume the recommended levels over time.
Limited sunlight
The body makes vitamin D3 when your skin is exposed to sunlight. There are numerous explanations to why someone may not get the needed sun exposure – for example, those who are homebound, live in northern latitudes, wear long robes or have a job that prevents them from getting much sunlight.
Kidney function
As you age, your kidneys are less able to convert vitamin D to its active form. This can result in a risk of vitamin D deficiency. It may be that vitamin supplements are needed to top up your levels.
Overweight
Those who struggle with obesity can also have low vitamin D levels. Vitamin D is extracted from your blood by fat cells, altering its release into circulation. People that have a body mass index of 30 or greater are more prone to low vitamin D blood levels.
A medical professional will typically conduct a blood test to measure your levels to test for a vitamin D deficiency. However, assessing vitamin levels is not a routine check, so you will need to request it if you have any concerns.
How to Ensure You Get Sufficient Vitamin D?
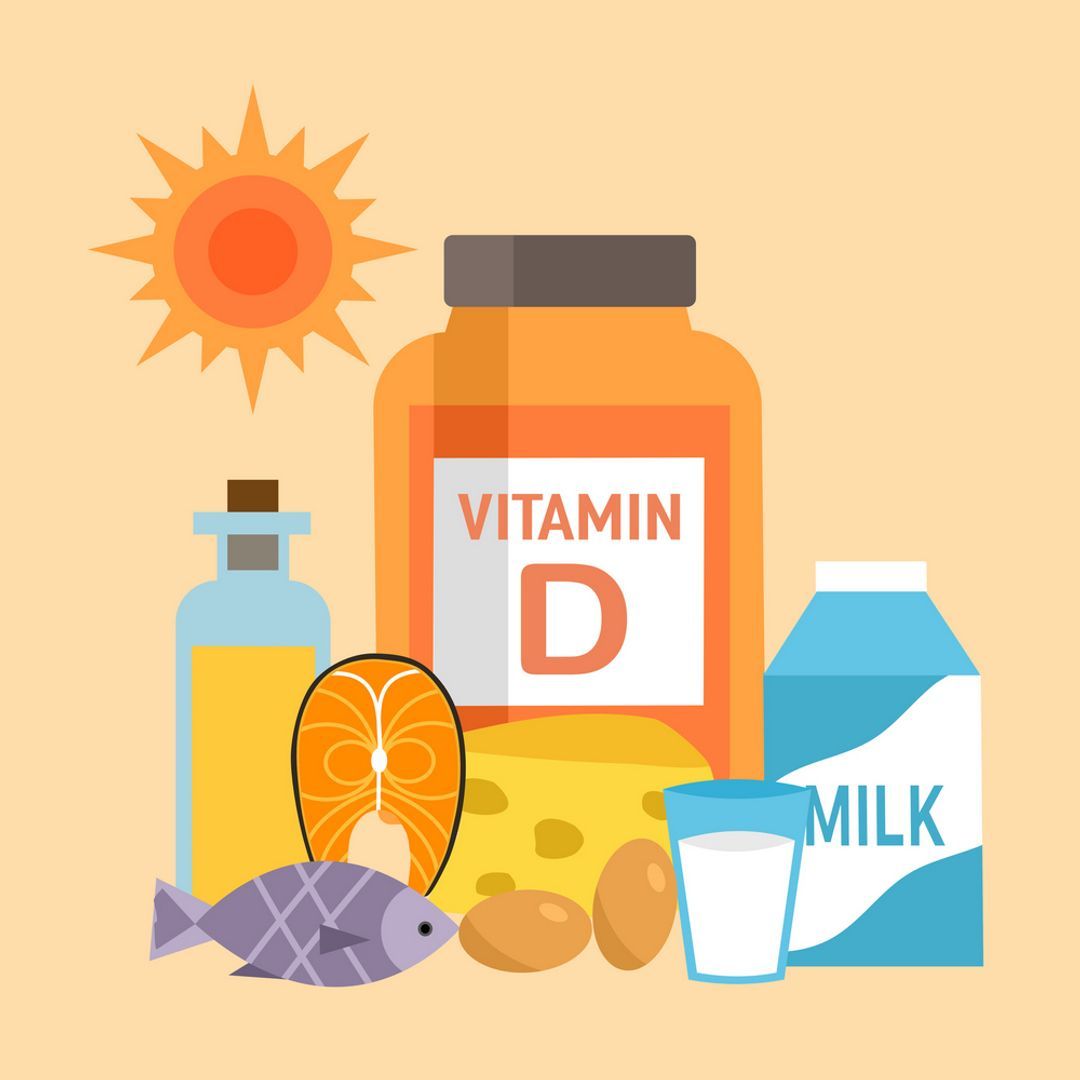

For people that follow a healthy lifestyle, the amount of vitamin D they need each day will vary by age. If you develop a health condition, such as osteoporosis, you may require different quantities. Older people may also require higher doses of vitamins due to their bodies not absorbing as sufficiently as they once did.
We can get vitamin D in a variety of ways, including the following:
Exposing our skin to the sun
Although we need to be careful not to damage our skin in the sun, there are benefits to moderate sunlight exposure. Our bodies produce Vitamin D3 when our skin is exposed to the ultraviolet B (UV-B) radiation the sun emits. The quantities of vitamin D3 our bodies are able to create will depend on a variety of factors such as the season, time of day, cloud coverage and air pollution, and where you live. It is worth noting that the sun's rays tend to be most powerful between the hours of 10:00 and 15:00.
The melanin skin content
Melanin is the brown/black pigment found in our skin, hair and eyes. Melanin is also what causes the skin to tan. Research has found that the darker your skin, the more sun exposure is needed to get sufficient amounts of vitamin D.
Eating foods with vitamin D
There are not many foods that have naturally occurring vitamin D. This is why we have developed foods with added vitamins. Modern food nutrition labels will show the number of vitamins contained within them. Foods which do contain vitamin D include oily fish, eggs, red meat, liver, egg yolks, and mushrooms which have been exposed to high levels of sunlight.
The goals of preventing and treating the lack of vitamin D are pretty much the same – to reach and maintain adequate vitamin D levels in the body. To make sure your vitamin intake is healthy, try to eat foods that contain vitamin D and get moderate sun exposure. Unfortunately, sunscreen or standing behind a window will prevent vitamin D from being produced by the skin. So when you go outside, be careful not to be out for too long. If you are very sensitive to UV-B, taking an appropriate vitamin D supplement may be safer.
There have been some links between vitamin D deficiency and accelerated skin ageing, although much more research is needed. However, some studies indicate that vitamin D plays a central role in skin protection and rejuvenation. It may also enhance your immune system and help fight off the free radicals which cause premature ageing.
What is known is that having sufficient vitamin D3 will help support your body as you grow older. Having a healthy body will help you enjoy your later years and allow you to continue living an active life.
Take Control of Your Health With a GlycanAge Test
Understanding how vitamin D3 supports anti-ageing is just one piece of the puzzle. To see how your lifestyle and internal health are truly impacting how you age, consider measuring your biological age with the GlycanAge Test.
It’s a science-backed way to understand your body’s ageing process and how to slow it down. Gain valuable insights into your immune system health with personalised recommendations to help you age better, all through a simple at-home test supported by expert guidance.
FAQ
Does vitamin D3 help you look younger?
Vitamin D is one of the best vitamins for skin health and provides anti-ageing properties. The other vitamins that are good for your skin include vitamins C, E, and K. Ensuring you are getting enough vitamins can help keep your skin looking and feeling youthful.
Can Vitamin D Reverse Wrinkles?
Vitamin D is understood to help with fine lines and wrinkles through its ability to work as an antioxidant. As you age, your telomeres (the part of human cells that affect how our cells age) shorten. Some research papers have reported that low vitamin D levels were associated with shorter telomeres.
How much vitamin D3 should I take for bone health?
The majority of adults should get somewhere between 600 to 800 international units (IU) of vitamin D every day. It should be noted that everybody is unique, and the amount of vitamin D2 produced by your body will vary depending on environmental and genetic factors.
Is vitamin D Good for Skin?
Due to vitamin D's antioxidant properties, it may help stimulate the growth of collagen and elastin. Healthy vitamin D levels do have the potential to prevent premature ageing, but too much sun can accelerate skin ageing.
How much vitamin D3 is too much for a senior?
The amount of vitamin D3 a senior person needs will vary. You may experience some unpleasant side effects of vitamin D toxicity that build up in your blood. It can cause nausea, vomiting, weakness and frequent urination.


