What Can Low Back Pain Tell Us About Our Health – and How to Manage It?
Changes in glycans point to chronic inflammation as a possible long-term underlying cause of low back pain and fatigue, even if there is no injury to the tissue.
By The GlycanAge Team
The male and female reproductive systems involve a complex network of processes that require a delicate balance in order to function optimally. While the reproductive systems of both genders have a unique composition of organs with different functions, both are equally important in enabling procreation.
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) is a hormone produced in the pituitary gland in the brain. It is responsible for healthy sexual development and reproductive function in males and females. Having a healthy balance of FSH circulating in the bloodstream is important in maintaining optimal reproductive health. Insufficient or excessive levels of FSH can lead to complications that affect the reproductive system.
If you suspect you have a reproductive disorder resulting from abnormal FSH levels, your doctor may recommend you take an FSH blood test. This article explores FSH blood tests in greater detail, including how they work, what they’re used for, who should get tested, and what the results mean. Keep reading to learn more.
The pituitary gland is a pea-sized organ in the brain that produces FSH.
In females, it plays an integral role in the maturation of ovarian follicles, which produce oestrogen and progesterone hormones to maintain the menstrual cycle and release eggs.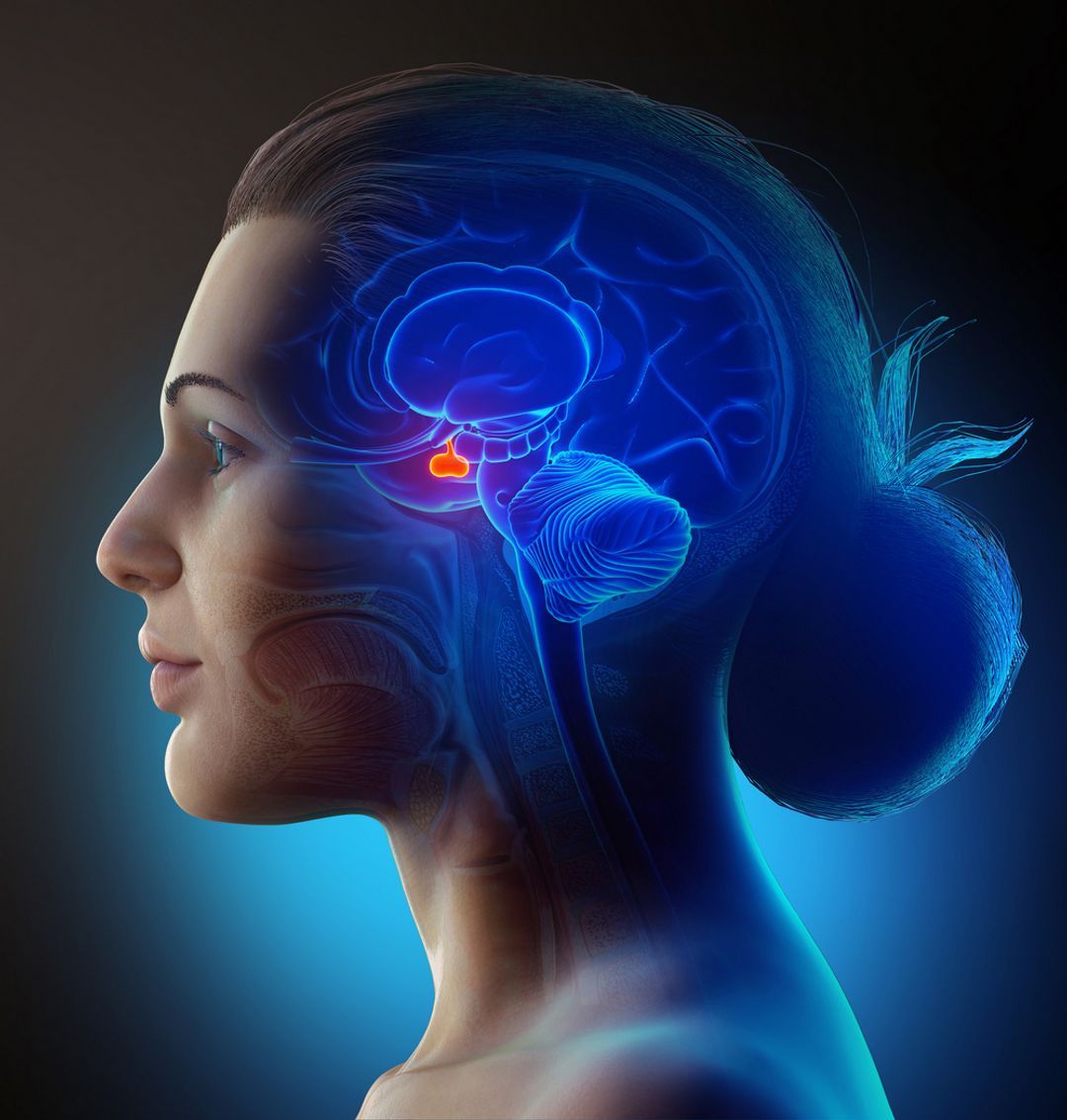
In males, it plays a crucial part in supporting sperm growth and gonad development.
In children, FSH levels remain low until they reach puberty, after which levels begin to rise to produce male and female sex hormones.
An FSH blood test measures the level of FSH present in the blood to find the underlying cause of symptoms affecting the reproductive system. Doctors usually check a person’s FSH levels to assess the following:
Their fertility
If they’re entering menopause
Irregular menstrual cycles
Early or delayed puberty
Pituitary gland disorders
However, an FSH blood test alone cannot diagnose reproductive conditions; it is typically used in conjunction with tests that detect other hormones, such as oestrogen, luteinizing hormone (LH), oestradiol, progesterone, or testosterone, to investigate such issues.
FSH and LH work in conjunction to regulate sexual and reproductive functions. For this reason, FSH and LH blood tests are usually taken together to determine the root cause of problematic symptoms.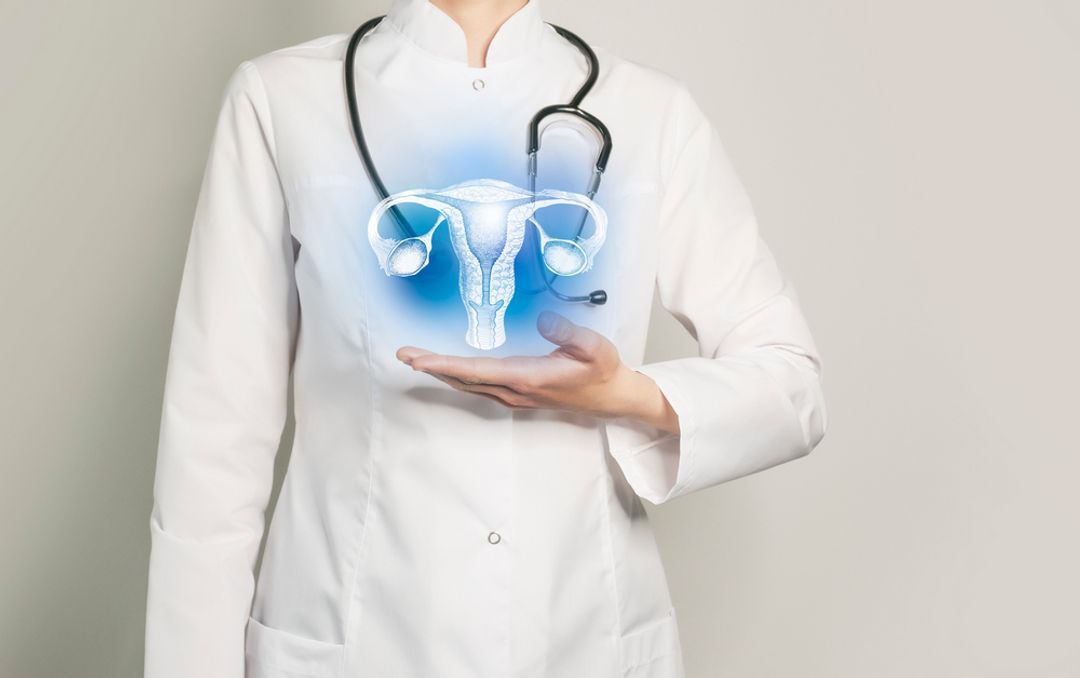
The FSH blood test has several purposes, depending on who it is performed on.
In women, the test is used to evaluate:
The start of menopause (perimenopause) in women aged 40-45 with menopausal symptoms
Early menopause in women under 40 with symptoms such as absent or erratic periods
Difficulty conceiving
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Ovarian failure
Abnormal vaginal or menstrual bleeding
Pituitary disorders
In men, the test is used to evaluate:
Infertility
Low sperm count
Low testosterone (hypogonadism)
Underdeveloped or no testicles or testicular failure
Pituitary disorders
In children, the test is used to evaluate:
An early start to puberty, (high FSH)
A delay in starting puberty(low FSH)
A height that is shorter or taller than expected
Men and women displaying symptoms of a pituitary gland disorder may benefit from an FSH blood test. Signs to look out for include:
Fatigue
Weakness
Weight loss
Decreased appetite
Men with a decreased sex drive or low muscle mass who have had difficulty getting their partner pregnant after 12 months of trying may also consider getting tested.
Women who have been unable to get pregnant after 12 months of trying, haven’t had a period, or had irregular periods for three or months may also need to get tested.
Doctors may also order an FSH blood test for a boy or girl entering puberty earlier or later than expected. Delayed onset of puberty is characterised as occurring after age 13 in girls and age 14 in boys. Children showing early signs of puberty (before age 9 in girls and age 10 in boys) may experience the following early signs
Breast enlargement in girls
Menstruation in girls
Testicle and penis growth in boys
Growth of pubic hair
While no special preparations are needed before taking an FSH blood test, women of childbearing age who have regular periods may need to have the test done in the first four days of their cycle.
If the test is to help diagnose menopause, it can be taken at any time of the month; however, repeat samples may be needed as initial results may be contradictory when menopause initially begins. This is because ovaries stop working gradually over several years.
Additionally, let your doctor know if you’re taking any prescription or non-prescription medications, including vitamin and herbal supplements and birth control, as they may affect test results.
During an FSH blood levels test, a qualified healthcare professional will administer the test in the same way as other traditional blood tests. The entire procedure takes less than five minutes.
You may feel slight pain or bruising in the area where the needle was inserted; this is temporary and nothing to be concerned about.
FSH blood test results are usually available within a day or two of providing your blood sample and may vary based on gender, age, health history, and other factors.
FSH levels are measured in milli-international units per millilitre (mIU/ml).
The normal range of FSH levels in females is:
0-4 mIU/ml before puberty
0.3-10 mIU/ml during puberty
4.7-21.5 mIU/ml during menstruating years
25.8-134.8 mIU/ml after menopause
The normal range of FSH levels in males is:
0-5 mIU/ml before puberty
0.3-10 mIU/ml during puberty
1.5-12.4 mIU/ml during adulthood
It is important to note that high or low FSH levels detected by blood tests are not a diagnostic tool for reproductive conditions but can indicate the underlying cause, along with other hormone tests.
FSH blood tests are usually performed at a doctor’s office, hospital, or another clinical setting. You usually require a doctor's referral to check your FSH levels.
You can also measure FSH levels at home with a urine test. Such tests are typically designed to check for high FSH levels and are indicated for women displaying symptoms of perimenopause and menopause, such as vaginal dryness, irregular periods, and hot flashes. The test will not diagnose such conditions. You should consult your doctor if the test returns a high FSH result.
At-home FSH test kits are available from testing.com, Flowflex, and Home Health UK.
Maintaining a healthy reproductive system is important for the purposes of procreation and protection from various health problems, including disease, infection, and dysfunction. While an FSH blood test is beneficial in helping to detect problems with reproductive and sexual health, it can only do so once problematic symptoms have begun to develop.
Age is the biggest risk factor for disease, and a GlycanAge test can accurately predict your likelihood of developing chronic disease by determining your biological age (the age of cells within your body). It does so by analysing the state of your immune system, that is, the extent of inflammation in your body.
Knowing your biological age can empower you to make the necessary lifestyle changes to effectively reduce your risk of chronic disease, increase your healthspan, and delay ageing.
All it takes is a finger-prick blood test in the convenience of your home to learn your biological age. Results are available in as little as three weeks of mailing your sample to our lab.
Various packages and price plans are available depending on your budget and health goals. Every test you purchase comes with a complimentary 1-1 session with a scientist and/or healthcare professional to help you understand your result and receive tailored advice on how to increase your healthspan and delay the ageing process.
Invest in your health and order your GlycanAge home test kit today.
By The GlycanAge Team

Start or continue your GlycanAge journey
Don’t be afraid to reach out to us and ask questions, provide commentary or suggest topics.
Other articles you may like:
Changes in glycans point to chronic inflammation as a possible long-term underlying cause of low back pain and fatigue, even if there is no injury to the tissue.
Ageing, whilst wholly a natural process, isn’t necessarily something we would want to embrace. Advancing age is a risk factor for heart disease, declining metabolic function, certain cancers, and a myriad of other conditions of poor health.