Bones play an important role in our body, providing vital support to muscles to help us move, protecting internal organs, and storing calcium. But did you know the structure of our bones is continuously changing?
Cells in the body constantly break down old bone and replace it with new bone; however, as we get older, the rate at which bone matter is replaced gradually declines, leading to decreased bone mass and strength.
Preserving bone mass is crucial to living a healthful life as we age. If bone health is left unchecked, it can lead to osteoporosis; a condition characterised by weak and brittle bones that are susceptible to breaking and fractures.
A bone density test is used to assess bone quality to determine your risk of osteoporosis. Keep reading to learn more about taking a bone density test to determine age, how it works, who should get tested, and much more.
What Is A Bone Age Test?
A bone density age test, also called a DEXA scan, uses low-dose x-rays to examine how dense your bones are by measuring the amount of calcium and other minerals present in the bone.
Such tests can effectively identify thinning bones - a condition known as osteopenia, which increases your risk of osteoporosis. With this condition, bones become progressively weak and fragile to the extent that even a small bump or minor fall can potentially cause a fracture.
Bone density testing can be used to: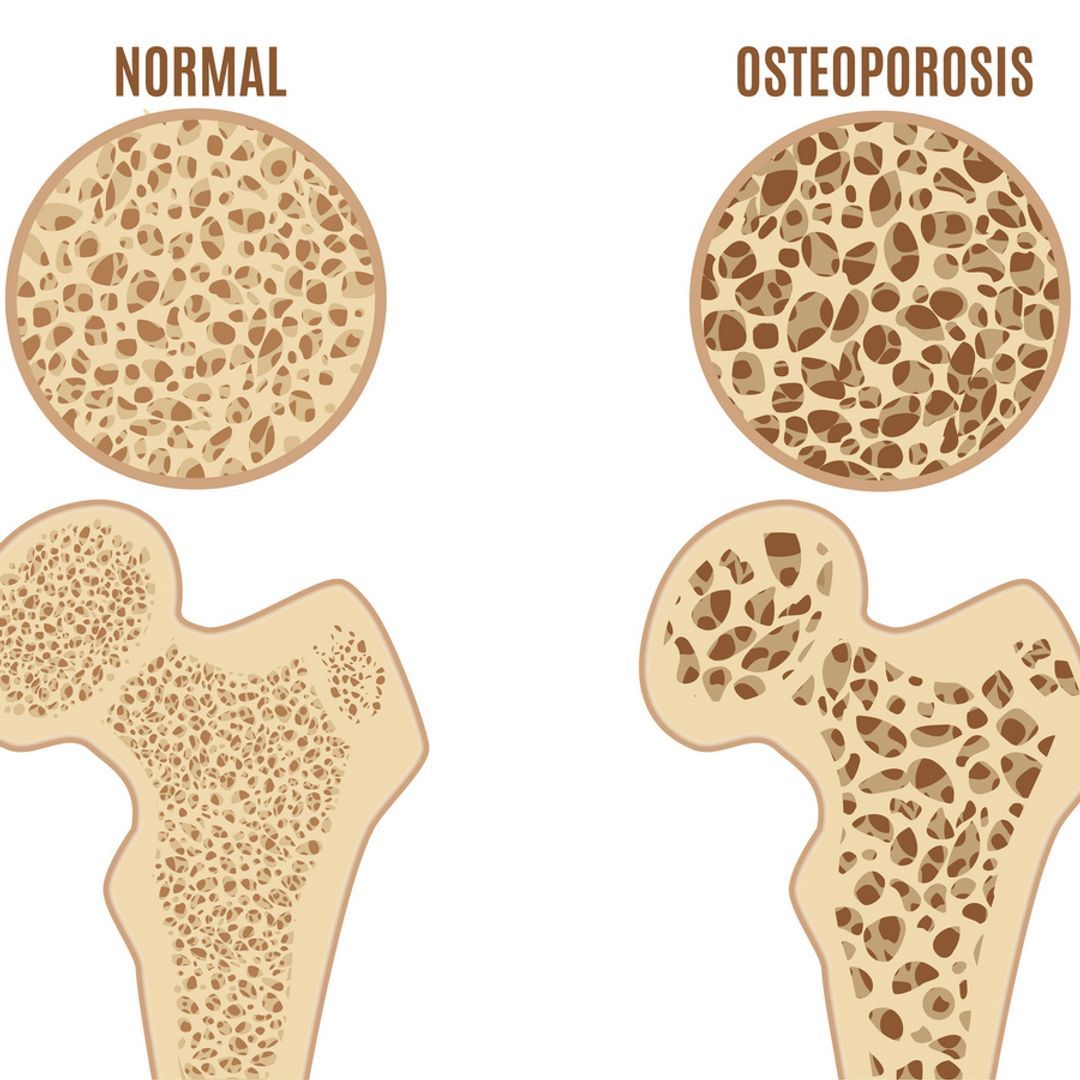
- screen for and diagnose osteoporosis in its earliest stages, long before a fracture has occurred
- estimate your chances of breaking a bone in future
- determine your rate of bone loss
- allow you to receive medical treatment to reduce your likelihood of fractures over time
- examine the effectiveness of any treatment you’re receiving.
How Does A Bone Age Test Work?
A DEXA scan is the most efficient and accurate method to scan for bone density. The procedure lasts around 20 minutes and involves the body being exposed to a low level of radiation to examine the mineral density of specific bones; most of this radiation is absorbed by body tissue.
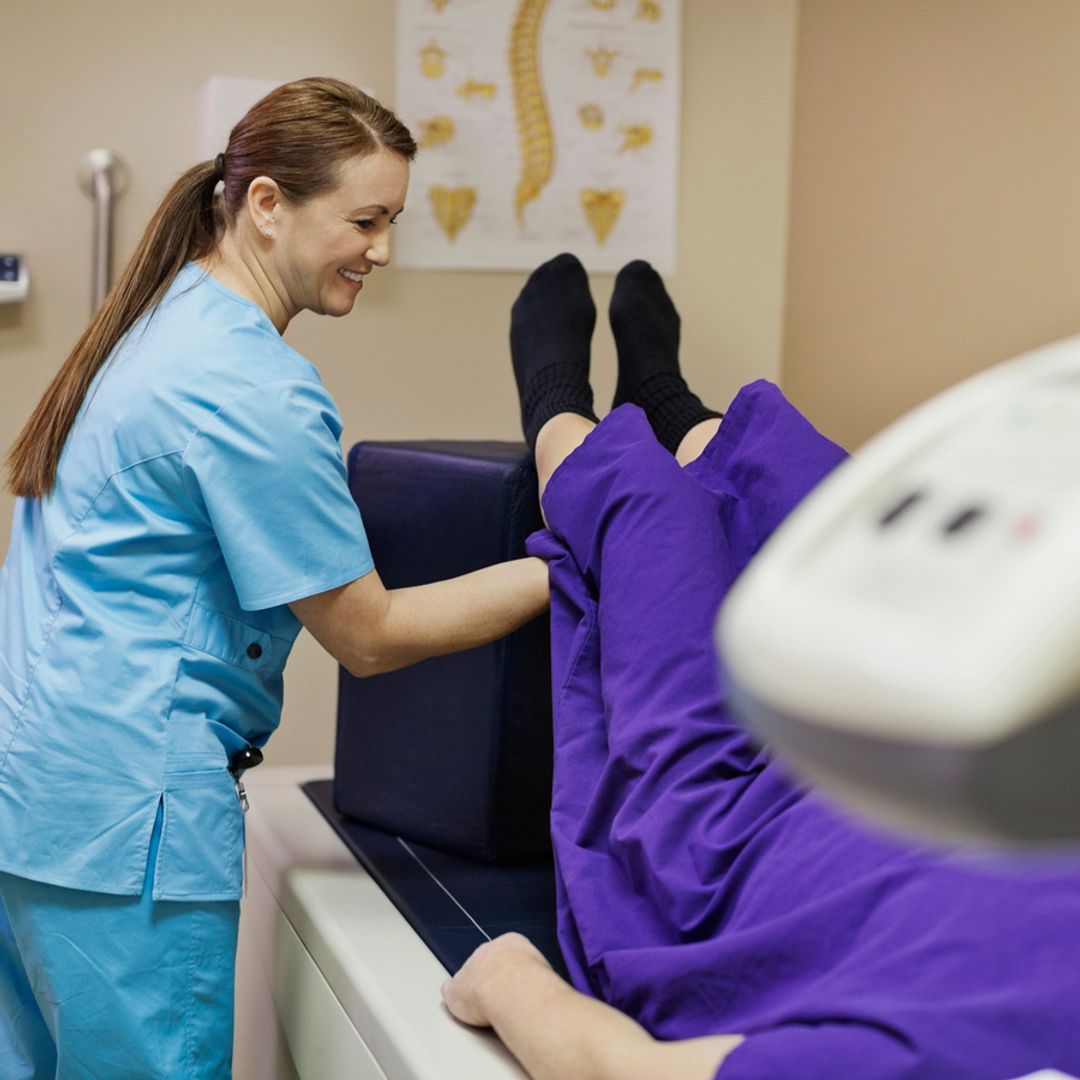 The test requires you to lie flat on your back on an open x-ray table as a large scanning arm passes over your body. Low-dose x-rays are beamed at specific areas with the highest risk of fracture, including the hips, spine, and lower arm, to assess bone strength and mass.
The test requires you to lie flat on your back on an open x-ray table as a large scanning arm passes over your body. Low-dose x-rays are beamed at specific areas with the highest risk of fracture, including the hips, spine, and lower arm, to assess bone strength and mass.
The information detected by the x-rays is then sent to a computer to produce various images and graphs of the scanned areas. Based on the results provided by the scan, the physician will write up a report recommending what treatment, if any, is most appropriate.
Why Is A Bone Age Test Important?
Bone density age tests are important because they alert you to issues relating to bone health that would have otherwise gone undetected. Osteopenia and osteoporosis have no outward symptoms; therefore, people are usually unaware they have the condition until they break or fracture a bone.
Bone fractures diminish a person’s quality of life, causing chronic pain, depression, disability, and deformity. Many people often never regain their ability to walk without aid and require lifelong care.
Knowing your exact risk for such conditions can empower you to take proactive measures to prevent fractures from occurring in the first place. By measuring the strength and mass of your bones, bone age tests identify potential problems with your bones before they progress into the fracture stage, at which point it is often too late to seek treatment.
Who Should Get A Bone Age Test?
The denser your bones, the stronger and less likely they are to break. With that said, those with a higher risk of osteopenia and osteoporosis should get a bone density test every two years as part of a routine health check.

Those who are particularly vulnerable to weak and brittle bones include:
- People over 50
- People under 50 who have a higher risk, i.e. smokers, heavy drinkers, or those with previously broken bones
- Postmenopausal women
- People with low sex hormones, i.e. cancer patients
- People taking certain medications, i.e. steroid drugs
- People who have lost at least 1.5 inches in height
- People with rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, hyperthyroidism, or chronic malnutrition
- People with a family history of osteoporosis
- People with low vitamin D or calcium levels
- People with a low body mass index
Where Do You Get A Bone Age Test?
To receive a bone age test, you will need a referral from your doctor or healthcare provider, who will consider the abovementioned factors when deciding if you require a DEXA scan.
If you want a bone density test, you need to contact your doctor and ask them to refer you to a hospital radiology department or private accredited facility.
It is important that the person performing the test is qualified to do so and can interpret the data correctly; you may want to confirm the staff member is accredited by the International Society for Clinical Densitometry (ISCD).
Take Control Of Your Health With A GlycanAge Test
Bone density tests are a valuable tool to measure bone strength and health, alerting you to any potential problems with your bones before you sustain a fracture. However, such tests only provide information on one aspect of your health; for a more comprehensive evaluation of your health status, you may consider taking a biological age test from GlycanAge.
The GlycanAge biological age test analyses biomarkers called glycans to assess the state of your immune system and accurately identify your risk for certain conditions. Glycans are proteins that form part of the immune system and play a major role in keeping us healthy.
The older you get, the more damage you accumulate in your body, thus increasing your pro-inflammatory glycans and making you more susceptible to major disease. By effectively preempting health conditions before they’ve developed, the GlycanAge test gives you a greater chance to prevent illness and disease before they can progress.

When you purchase a GlycanAge test, you get a complimentary 1-1 consultation with a team of scientists and qualified healthcare professionals to accurately interpret your results and provide practical advice tailored to your distinct health needs on how to reverse your biological age.
Several packages are available to buy, depending on where you are on your wellness journey. If you simply want to determine your current biological age, you may consider buying a single test. Two tests are recommended for those who want to track their health progress over time. A custom plan is also available to those who are invested in their health over the long term, such as biohackers or professional athletes.
Once you’ve ordered your home testing kit, all you need to do is provide a finger-prick blood sample and submit it to the accredited laboratory. Your personalised report containing your results will be available in as little as 3-5 weeks.
Invest in your health and order your GlycanAge biological age test today.


 The test requires you to lie flat on your back on an open x-ray table as a large scanning arm passes over your body. Low-dose x-rays are beamed at specific areas with the highest risk of fracture, including the hips, spine, and lower arm, to assess bone strength and mass.
The test requires you to lie flat on your back on an open x-ray table as a large scanning arm passes over your body. Low-dose x-rays are beamed at specific areas with the highest risk of fracture, including the hips, spine, and lower arm, to assess bone strength and mass.

